Estimated Reading Time: 6 minutes
|As they say: “Your body is your temple”; but the chaos of modern life can weigh it down. From nonstop schedules and processed foods to environmental toxins and stress, you're constantly exposed to triggers that disrupt your natural balance.
Over time, these everyday habits can quietly lead to inflammation, impacting both your body and mind without obvious signs. You may feel bloated, tired, foggy, or simply not like yourself. Believe it or not; it starts in your gut, but soon it affects everything, your immunity, mood, and overall well-being.
The good news is; you can support your body’s recovery with something as simple as food. The right nutrients can help bring your system back to balance, naturally. In this blog, you’ll discover eight powerful anti-inflammatory foods and how adding them to your plate can help restore your internal harmony, one bite at a time.
What Is Inflammation?
Inflammation can be understood as the foundation of every disease. It is your body's natural defense system, the process by which the white blood cells (fighter cells) protect you. It is activated when your immune system identifies harmful invaders like pathogens, irritants, or injuries.
Now, let's see...
How Your Body Reacts to This
When your body detects an injury or infection, it sends these fighter cells to the affected area to help protect and heal. These cells release certain chemicals that increase blood flow, which can make the area feel warm and look red. Some of these chemicals also cause fluid to move into the surrounding tissues, leading to swelling. As a result, nearby nerves may get triggered, causing pain or discomfort.
There are 2 types of inflammation:
-
Acute inflammation: Short-term and often visible; like the swelling after a cut, is a sign that your body is healing. It's a helpful and necessary process.
-
Chronic inflammation: This long-term, often silent condition keeps your body in constant stress, with fighter cells perpetually activated.
Over time, this ongoing response can do more harm than good, disrupt healthy tissue, and contribute to various diseases.
The following factors can trigger chronic inflammation:
-
Poor dietary habits (refined sugar, processed meats, trans fats)
-
Sedentary lifestyle
-
Stress
-
Environmental toxins
-
Gut imbalances
-
Inadequate sleep
Over time, chronic inflammation can impact various systems in your body, silently deteriorating your wellness. Let’s learn more about what chronic inflammation can do to your body and mind.
How Can Inflammation Affect You?
Inflammation has been linked to a range of health issues. When it stays with you for too long, it can badly impact your major organs, such as your heart, liver, kidneys, lungs, brain, digestive system, and reproductive system. It can lead to tissue damage or disease in these organs if the inflammation doesn't resolve properly. It largely affects:
-
Your gut: Causing discomfort, bloating, and irregular bowel movements
-
Your energy: Persistent fatigue
-
Your skin: Flare-ups and dullness
-
Your mind: Brain fog, mood fluctuations
-
Your immunity: Frequent colds or allergies
To protect your body, you need to try to reduce inflammation. But are there ways to reduce inflammation? Yes! Explore them in the next section.
What Can You Do to Reduce Inflammation?
Managing inflammation is a lifestyle journey. A combination of mindful movement, sleep hygiene, stress management, and nutrition can help support your body. Among these, your diet plays the most consistent and controllable role. While no food or remedy can claim to treat or cure these issues, certain foods can support the body's ability to maintain balance and wellness.
Anti-inflammatory foods don’t suppress your immune system; they support your natural detoxification pathways, enhance gut balance, and help your body find its rhythm again.
8 Best Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Add to Your Diet
1. Turmeric
Turmeric, a golden root used in Indian cooking, contains curcumin, which supports your body’s inflammatory response. In a 2025 article published in Frontiers in Pharmacology, the writer commented that curcumin may help support oxidative balance, which is closely linked to inflammation control.
Pro tip: Always consume turmeric with a pinch of black pepper to improve absorption.
2. Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale, Swiss Chard)
These greens are rich in antioxidants, magnesium, and vitamins A, C, and K. They support cellular detox and are high in polyphenols, compounds that help maintain cellular harmony.
Did you know? Magnesium deficiency has been associated with heightened inflammatory signals.
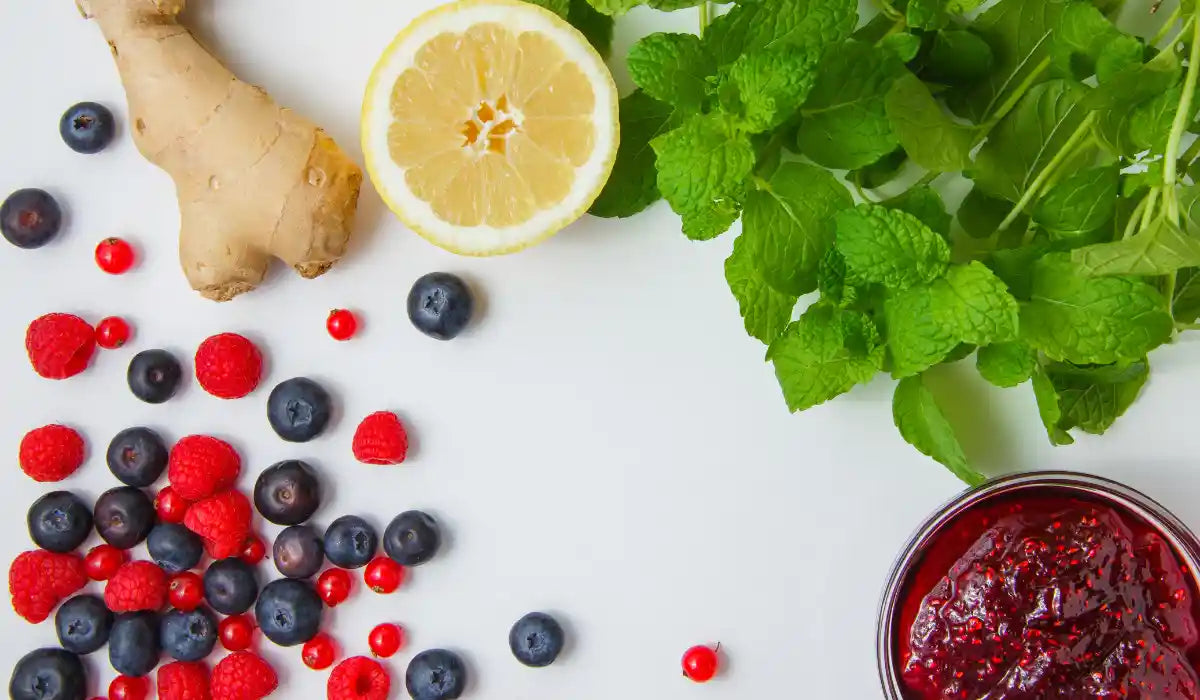
3. Berries (Blueberries, Strawberries, Raspberries)
Berries are rich in anthocyanins, which support your body's inflammatory balance. These compounds are known for helping manage oxidative stress, a key player in chronic inflammation.
According to a 2022 article, Berry polyphenols may help reduce inflammation by supporting a healthy gut and turning off certain inflammatory pathways. They're considered promising natural compounds for managing inflammation-related diseases, but more research is still needed to understand how they work and ensure their safe use fully.
4. Ginger
Gingerol, the bioactive compound in ginger, supports digestive health and promotes metabolic function. When your digestion works efficiently, your inflammatory response may stay balanced too.
Tip: Ginger tea after meals may aid in better digestion and comfort.
5. Fatty Fish (Salmon, Sardines, Mackerel)
These fish contain omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA) that help support the production of anti-inflammatory molecules. As per research, omega-3 fats may be associated with supporting immune modulation and balancing inflammation markers.
Plant alternative: Flaxseeds and chia seeds.
6. Olive Oil (Extra Virgin)
Rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, olive oil supports cardiovascular wellness and cellular protection. It also promotes gut health, which plays a central role in inflammation control.
Use: Drizzle on salads or use as a finishing oil over cooked veggies.
7. Nuts and Seeds (Walnuts, Almonds, Flaxseeds, Chia Seeds)
These are nutrient powerhouses full of fiber, protein, omega-3s, and antioxidants that support your overall well-being and may help in calming your body’s inflammatory reactions.
Did you know? Walnuts are especially rich in alpha-linolenic acid, a plant-based omega-3 fat, and are excellent for heart health.
8. Green Tea
With the powerful antioxidant, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), Green Tea helps your metabolism and manages free radicals in your body. One must sip freshly brewed green tea instead of bottled options available in the market for better results.
Conclusion
When it comes to your body, you should be more careful. Problems like inflammation can be managed through supportive nutrition, movement, rest, and mindfulness. All these together can help reduce its toll on your body and mind. All these anti-inflammatory dietary options can help you manage it in a simple, sustainable way.
Small changes, like adding berries to your breakfast, sipping green tea post-lunch, or switching to olive oil or prescribed natural supplements, can add up. Small changes can help you keep your body young and healthy. Try changing your lifestyle and your dietary choices and see the difference in yourself.
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. This blog is for informational purposes only and is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
References
-
Bouyahya, A. et al. (2022) 'Chemical compounds of Berry-Derived polyphenols and their effects on gut microbiota, inflammation, and cancer,' Molecules, 27(10), p. 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103286.
-
Cheng, M. et al. (2025) 'Exploring the role of curcumin in mitigating oxidative stress to alleviate lipid metabolism disorders,' Frontiers in Pharmacology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2025.1517174.